Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
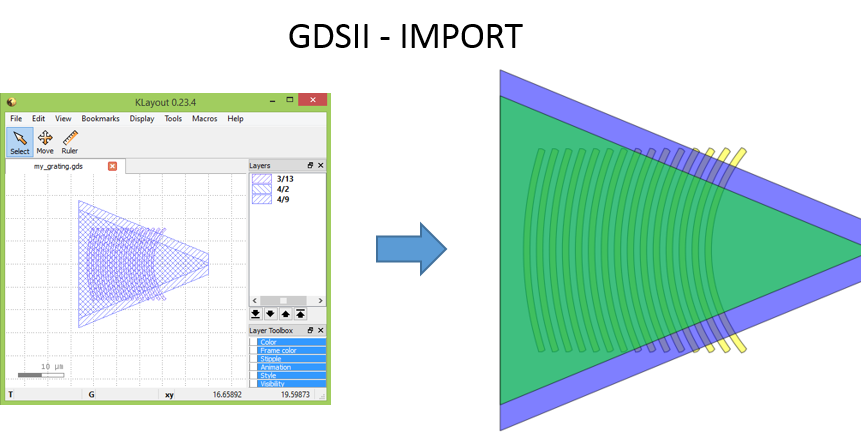
Creating a Cell from an existing GDSII file with a new technology
This sample illustrates how to port a GDSII file to a new technology.
There are cases when you want to integrate an existing old design into a new Ipkiss design, but where only the GDSII output is available. Ipkiss can wrap this GDSII file into an Ipkiss cell, and then you can manually add the ports, netlist and model so that you can use it into a larger circuit.
Note that all the layers used in the GDSII must first be defined in the Technology file. This may not always be the case. To solve this we create a new technology file based on an existing tech file and add the missing layers.
Importing from GDSII
Illustrates
Create a new technology and add the missing layers so that you can import them.
How to run this example
To run the first example, you will need mytech.py and my_grating_with_new_layers.gds
Adding the missing layers to a tech file
Technology example which starts from the si_fab PDK in IPKISS. As the layers existing in your GDSII files may not be in the si_fab TECH, we will add them to the technology here. Each layer needs to be a ProcessPurpose layer. Here we will add two layers that use the 1 process. In the long run it is best to create your own TECH file for your process: si_fab is a good example but Luceda can do it for you as service.
import si_fab.all as pdk
import ipkiss3.all as i3
TECH = i3.TECH
TECH.name = "CUSTOMIZED TECHNOLOGY SAMPLE"
from ipkiss.process import ProcessLayer, ProcessPurposeLayer, PatternPurpose
from ipkiss.technology.technology import TechnologyTree
from ipkiss.visualisation.display_style import DisplayStyle, DisplayStyleSet
from ipkiss.visualisation import color
# Create 1 new process and 2 new purposes and add them to the TECH tree
new_process = ProcessLayer(name="NEW_PROCESS", extension="NEWP")
new_purpose_1 = PatternPurpose(name="PATTERN_1", extension="PAT_1")
new_purpose_2 = PatternPurpose(name="PATTERN_2", extension="PAT_2")
TECH.PROCESS.NEW_PROCESS = new_process
TECH.PPLAYER.NEW_PROCESS = TechnologyTree()
# Combine the process and purposes into PPlayers and add them to the TECH tree.
TECH.PPLAYER.NEW_PROCESS.PP1 = ProcessPurposeLayer(process=new_process,
purpose=new_purpose_1,
name="PP1")
TECH.PPLAYER.NEW_PROCESS.PP2 = ProcessPurposeLayer(process=new_process,
purpose=new_purpose_2,
name="PP2")
# Add the layer to the GDSII import/export rules.
# These are the GDSII process and purpose numbers used in your existing gdsii files.
gdsii_maps = {(new_process, new_purpose_1) : (99, 1),
(new_process, new_purpose_2) : (99, 2)}
TECH.GDSII.LAYERTABLE.update(gdsii_maps)
# add the layer to the visualization styleset
DISPLAY_PP1 = DisplayStyle(color = color.COLOR_YELLOW, alpha = 0.5, edgewidth = 1.0)
DISPLAY_PP2 = DisplayStyle(color = color.COLOR_YELLOW, alpha = 0.2, edgewidth = 1.0)
TECH.DISPLAY.DEFAULT_DISPLAY_STYLE_SET.append((TECH.PPLAYER.NEW_PROCESS.PP1, DISPLAY_PP1))
TECH.DISPLAY.DEFAULT_DISPLAY_STYLE_SET.append((TECH.PPLAYER.NEW_PROCESS.PP2, DISPLAY_PP2))
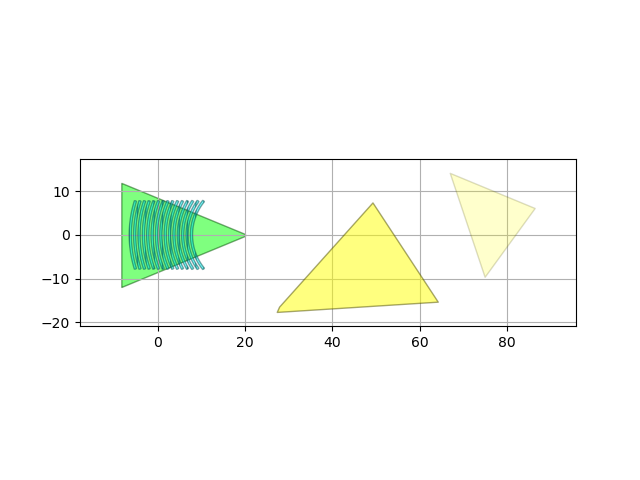
Importing a cell with GDSII layers in the new tech file
This sample illustrates how to import a Cell from an existing GDSII file Since all the layers used in the GDSII file are present in silicon_photonics TECH. we append it the technology with the layers we want. Appending an existing TECH is easier than creating TECH file from nothing. Nevertheless, you may want to do that as this is the most stable option in the long run.
# 1. Import the appended technology
import mytech # noqa
from ipkiss3 import all as i3
# 2. Define a cell that imports the written GDSII, and:
# - add ports
class ImportedGrating(i3.GDSCell):
def _default_filename(self):
return "my_grating_with_new_layers.gds" # path to the gdsii file that contains the cell to be imported
def _default_cell_name(self):
return "unique_grating_name_used_in_GDSII" # name of the cell to be imported inside the gdsii file.
class Layout(i3.GDSCell.Layout):
def _generate_ports(self, ports):
ports += i3.OpticalPort(
name="in",
position=(20.0, 0.0),
angle=0.0,
) # We have to manually set the ports as this info is not in the gdsii file yet
ports += i3.VerticalOpticalPort(
name="vertical_in",
position=(0.0, 0.0),
inclination=90.0,
angle=0.0,
) # For the fiber a vertical port is used.
return ports
Instantiate the imported cell with its Layout view and write it back to GDSII.
im_cell = ImportedGrating(name="my_grating")
im_layout = im_cell.Layout()
im_layout.visualize()
im_layout.write_gdsii("my_grating_with_new_layers_rewritten.gds")